Overview
Task
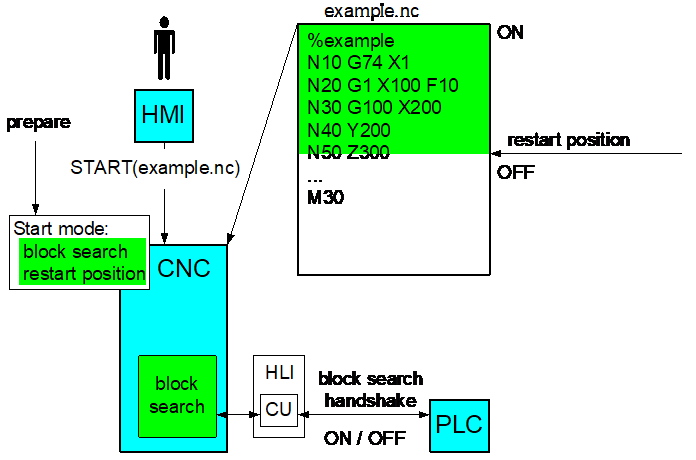
The operator can start machining at what is called the continuation position at any point in the program. After a program is interrupted (e.g. tool breakage), this is a quick method to reactivate machining at the point of interruption.
The continuation position can be defined using a number of different block search types (file offset, block counter, block number, etc.).
It is imperative to restore the entire program context at the starting point specified here (program parameters, axis positions, etc.). This is ensured by processing the program up to this continuation position without any axis motion (simulation). Technology functions are signalled to the PLC, even during the simulation. All the vital machine functions for the machining process are then activated at the continuation position (e.g. coolant, velocity).
When the program reaches the continuation position, the axes can be moved to their current positions at this program position either manually or automatically.
The operator can then start the continued execution of the program.
Notice
Block search type 2 is no longer available.