Working on the conveyor system
Machining or handling takes place in the co-moving workpiece coordinate system PCS1. The programmed path is intersected on the conveyor movement. This means that programming a feed rate of F=0 mm/min in the co-moving system PCS1 results in a velocity that corresponds to the conveyor velocity vconv in the stationary coordinate system PCS0. In this case, the TCP moves at conveyor velocity.
This superimposition results in different maximum velocities on the workpiece and in the opposite conveying direction.
- In the conveying direction:
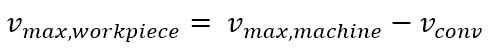
- In the opposite conveying direction:
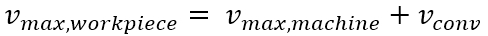
Starting from PCS1, other coordinate systems can be programmed using the #CS command. The workspace limits continue to be monitored as long as synchronisation with the conveyor is active. If a programmed contour crosses the workspace limit in the conveying direction, it can no longer be tracked and the program is aborted with an error message.
If the programmed contour crosses the workspace limit in the opposite conveying direction, the movement is adjusted so that the contour can be traversed without crossing the workspace limit.
See Monitoring the workspace limit in the opposite conveying direction.