Method for automatic memory layout (P-EXTV-00012)
P-EXTV-00012 | Method for automatic memory layout |
Description | As of CNC Build V2.10.1025.00 and higher, the CNC can automatically create the external variables in the memory without gaps. External variables can also be assigned to any memory address by using the parameter var[i].byte_offset P-EXTV-00002 or by selecting a 24-byte are via var[i].index P-EXTV-00038. If the automatic and manual address selection is combined, this parameters defines how the CNC generates the automatic addresses for the variables. |
Parameter | auto_memory_mode |
Data type | STRING |
Data range | START_VE_MEMORY: LAST_USED_ADDRESS: |
Dimension | ---- |
Default value | START_VE_MEMORY |
Remarks | This parameter is available as of CNC Builds 2.11.2027.01, V.2.11.2807.18 or V3.1.3052.01 and higher. Older CNC builds always use the START_VE_MEMORY setting. |
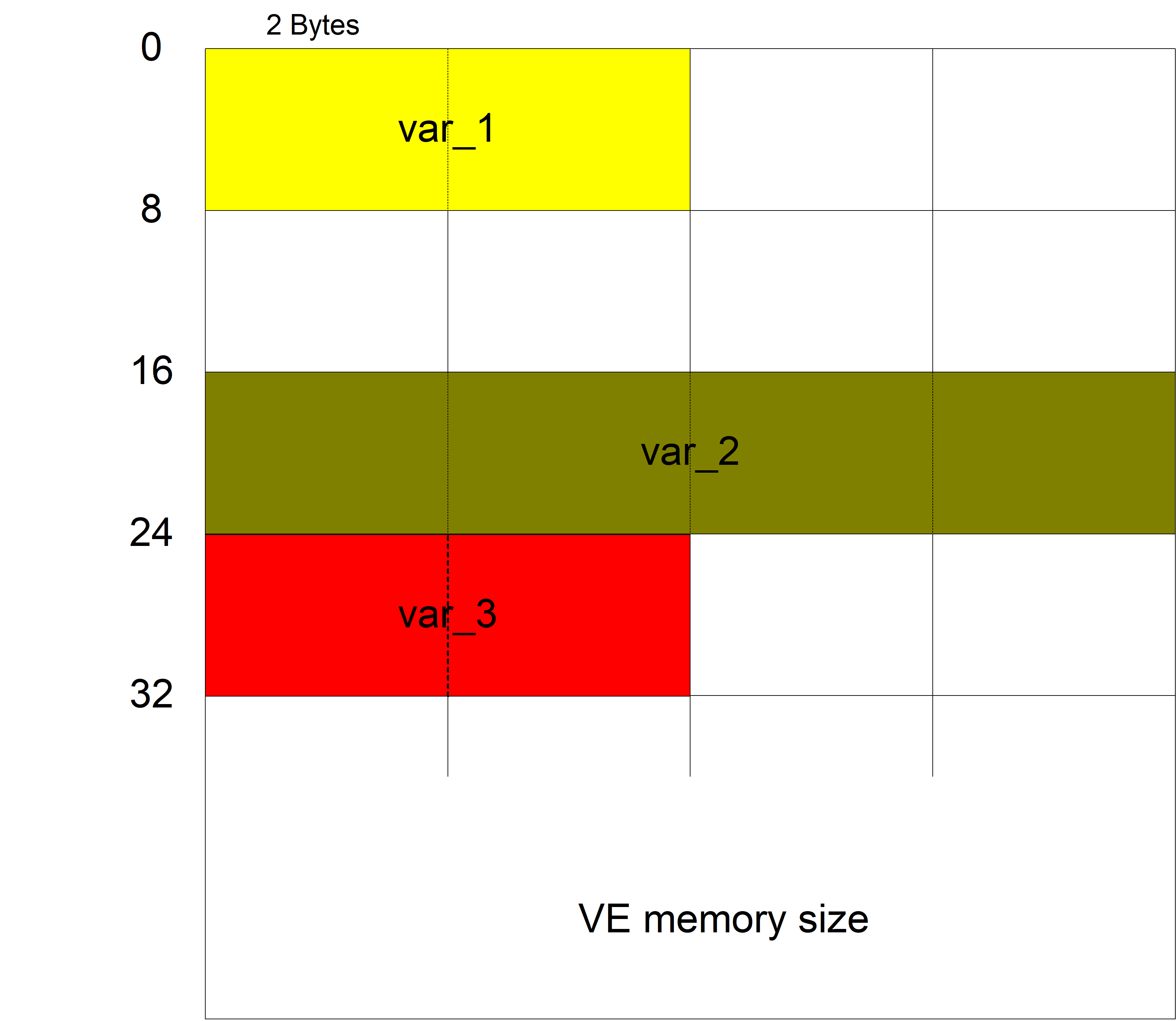
Example for auto_memory_mode = START_VE_MEMORY:
auto_memory_mode START_VE_MEMORY
var[0].name var_1
var[0].type SGN32
var[0].scope GLOBAL
var[0].synchronisation FALSE
var[0].access_rights READ_WRITE
#
var[1].name var_2
var[1].type REAL64
var[1].scope GLOBAL
var[1].synchronisation TRUE
var[1].access_rights READ_WRITE
var[1].byte_offset 16
#
var[2].name var_3
var[2].type SGN32
var[2].scope GLOBAL
var[2].synchronisation TRUE
var[2].access_rights READ_WRITE
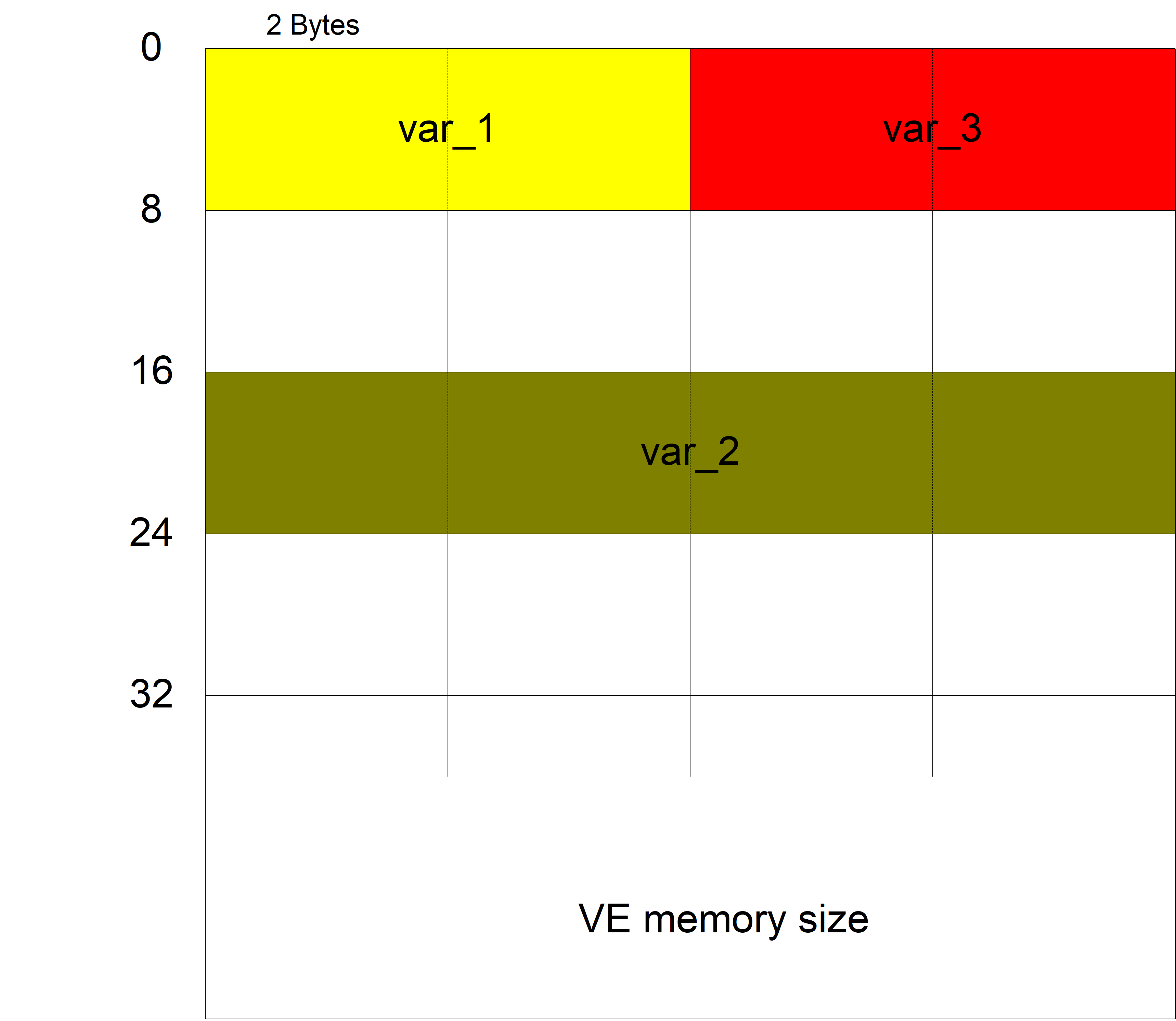
Example for auto_memory_mode = LAST_USED_ADDRESS:
auto_memory_mode LAST_USED_ADDRESS
var[0].name var_1
var[0].type SGN32
var[0].scope GLOBAL
var[0].synchronisation FALSE
var[0].access_rights READ_WRITE
#
var[1].name var_2
var[1].type REAL64
var[1].scope GLOBAL
var[1].synchronisation TRUE
var[1].access_rights READ_WRITE
var[1].byte_offset 16
#
var[2].name var_3
var[2].type SGN32
var[2].scope GLOBAL
var[2].synchronisation TRUE
var[2].access_rights READ_WRITE